BMC : Basics of Telecommunications(2)
BASICS OF Business Data Communication(2)
[1]. Data Flows with Different Line Configurations
1. Data Flows
1). Simplex : One way only
2). Half Duplex : One way, then the other
- data may travel in both directions, but only in one direction at a timedata may travel in both directions, but only in one direction at a timedata may travel in both directions, but only in one direction at a timedata may travel in both directions, but only in one direction at a timedata may travel in both directions, but only in one direction at a time
- provides non-simultaneous two-way communication
- computers use control signals to negotiate when to send and when to receive
- the time it takes to switch between sending and receiving is called turnaround time
3). Full Duplex : both ways at the same time
2. Transmission Mode
Unity of Info: A Character (Symbol), A Sample (Audio) and A Pixel (Graphics) How To Preserve Unity of Information during transmission ?
1). Parallel / Serial 모드
- Parallel(병렬) : n bits (multiple of 8) in 1 cycle
- Generic Communications Interface : Parallel(병렬)
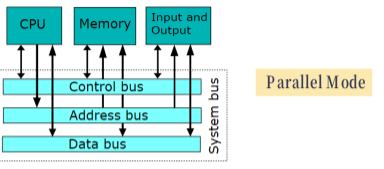
- Generic Communications Interface : Parallel(병렬)
-
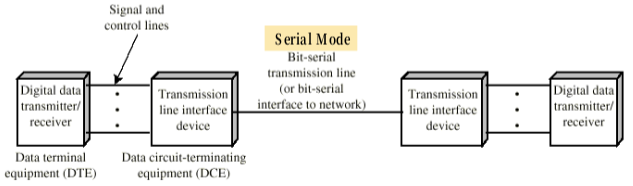
serial(직렬) : 1 bit in 1 cycle
- Asynchronous : start/stop bits per unit
- Synchronization occurs on the data link layer
- Synchronous : block of units
- Low-speed terminals and PCs commonly use asynchronous transmission
- inexpensive
- “burst” tendency of communication reduces impact of inefficiency Large systems and networks commonly use synchronous transmission
- overhead too expensive; efficiency necessary
- error-checking more important
- Low-speed terminals and PCs commonly use asynchronous transmission
-
상세
Asynchronous Transmission Synchronous Transmission Serial communication Parallel communication? 타이밍에러 누적시 문제발생 , 데이터링크 계층에서 동기화 됨, UART :RS232C, RS442, RS485 등 별도의 clock line 필요I2C 등, 전송효율, 속도높음 Data transmitted 1 character at a time, Character format is 1 start & 1+ stop bit, plus data of 5-8 bits Large blocks of bits transmitted without start/stop codes Character may include parity bit Data framed by preamble/postamble bit patterns Timing needed only within each character Synchronized by clock signal or clocking data Resynchronization each start bit More efficient than asynchronous Uses simple, cheap technology Used at higher speeds than asynchronous Wastes 20-30% of bandwidth Overhead typically below 5% -
정리
|구분|비동기식|동기식| |—|—|—| |통신속도|저속|고속| |회로복잡도|단순|복잡| |구축비용|저가|고가| |동기제어방식|START/STOP BIT|클럭동기| |전송단위|문자단위|블럭단위전송| |적용예|RS-232C|전화교환망, ATM, 데이터통신망| |||| - Generic Communications Interface : serial(직렬)
- Asynchronous : start/stop bits per unit
2). Data Link Layer – Managing Data Flow
-
OSI 모델
| ISO’s Open Systems Interconnection (OSI)| |—| | 1. Application Layer | | 2. Presentation Layer | | 3. Session Layer | | 4. Transport Layer | | 5. Network Layer | | 6. Data Link Layer – Managing Data Flow | | 7. Physical Layer – Managing Medium | -
Physical / Data link layer
|Physical Layer|Data link layer| |—|—| |Refers to transmission of unstructured bits over physical medium. Deals with characteristics of and access to the physical medium|Provides for reliable transfer of information across physical link| ||- - Data link layer includes :
- transmission of blocks of data (“frames”)
- synchronization
- error control
- flow control
- DTE/DTC :
- DTE : 데이터 단말장치(Data Terminal Equipment)
- DCE : 데이터 통신장치(Data Communications Equipment)
- 보통 PC는 DTE 장치이고 그 반면에 대부분의 다른 디바이스는 보통 DCE 장치임. DCE와 DTE 장치 RS-232 스탠더드에서는 DTE 장치는 25 핀의 male 커넥터를 사용하고, DCE 장치는 25 핀의 female 커넥터를 사용함. DTE장치를 DCE장치에 접속하는 경우에는 스트레이트 케이블을 이용
- Standard
- Communication card, UART(Universal Asynchronous Reciever Transmitter) RS-232-C, DB-25, DB-9, Moodem, RJ-11 ….
3. Flow Control
1). Flow control Timing needed only within each character
- Necessary when data is being sent faster than it can be processed by receiver
- Computer to printer is typical setting
- Can also be from computer to computer, when a processing program is limited in capacity
1). Stop-and-Wait Flow Control
- Simplest form
- Source may not send new frame until receiver acknowledges the frame already sent
- Very inefficient, especially when a single message is broken into separate frames
2). Sliding-Window Flow Control
- Sliding Window
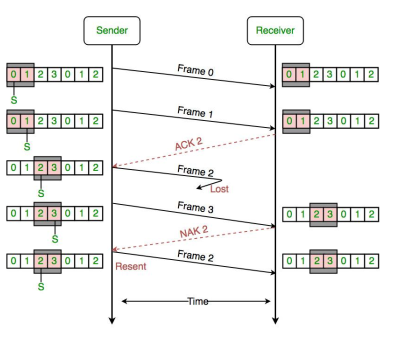
- Allows multiple frames to be in transit
- Receiver sends acknowledgement with sequence number of anticipated frame
- Sender maintains list of sequence numbers it can send, receiver maintains list of sequence numbers it can receive
- ACK (acknowledgement) supplemented with RNR(receiver not ready)
[2]. Communication Impairments
1. Threats to Communication Reliability
1). Threat
- 3 Types of Threats
|Reliability Threats
(Nature Caused Problems) |Security Threats
(Human Caused Problems)| |:—:|:—:| |Attenuations|| |Delay distortion|| |Noise|| - 참고자료(수업).1: Transmission Impairments 1 (6:57)
- 참고자료(수업).2: Transmission Impairments 2 (8:00)
2). Attenuation
- Measurement of attenuation, Decibel (dB)
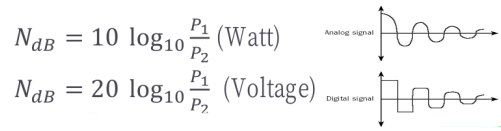
- Repeater for Digital signal
- Amplifier for Analog signals
- Amplifier increases the noise level as well
3). Delay distortion
- Various frequency components of a signal arrives at the Rx at different time on guided media
- Fix: Synchronization Techniques
- Propagation Delay= Distance/Signal Speed
4). Noise
- Noise Effects (SNR, Signal to Noise Ratio)
- The Shannon–Hartley theorem
- Max. Capacity= Bandwidth x Log 2 (1+ S/N)
- As data rate increases, error rate increases
- The Shannon–Hartley theorem
- Fix:
- Line conditioning
- Error Detection and Correction
5). Two components of Error control process
- All transmission media have potential for introduction of errors
- Error detection
- Error correction
2. How to detect impairment (errors)
- Three Error detection methods:
1). Parity check
- Even and Odd parity methods
- add 0 or 1 parity bit to each (7-bit ASCII) character in order to make the sum of the 8 bits even or odd.
- ex), G(1110001) → (11100011)
- Not fool proof, why?
2). Checksum(and LRC Error Detection)
- Sum ASCII decimal values of all characters in a block
- Divide this number by 255
- Put the remainder (checksum) into control characters
- Only synchronous transmission
- More than 99.9999 percent error detection
- for example, 128 A’s (1000001) in the block
3). CRC : Cyclic Redundancy Check
3. How to fix errors
- Two types of errors : ‘Lost frame’, ‘Damaged frame’
1). Fix: based on Automatic Repeat Request
- 1.1). Stop-N-Wait ARQ
- One frame received and handled at a time
- If frame is damaged, receiver discards it and sends no acknowledgment
- Sender uses timer to determine whether or not to retransmit
- Sender must keep a copy of transmitted frame until acknowledgment is received
- If acknowledgment is damaged, sender will know it because of numbering
- 1.2). Go-back-N ARQ (Sliding Window)
- Uses sliding-window flow control
- When receiver detects error, it sends negative acknowledgment (REJ)
- Sender must begin transmitting again from rejected frame
- Transmitter must keep a copy of all transmitted frames
2). Automatic Repeat reQuest (ARQ) ???
- 2.1). Error detection
- 2.2). Positive acknowledgment
- 2.3). Retransmission after time-out
- 2.4). Negative acknowledgment and retransmission
[3]. Security of Communication Human Threats to Communications
- CONFIDENTIALITY, INTEGRITY, NON-REPUDIATION 이 중요
|SECURE ?||
|:—:|:—|
|- CONFIDENTIALITY||
|- INTEGRITY|: 무결성 |
|- NON-REPUDIATION||
1. Security Control
- Passive/Active Thtreats
- Passive Threats: monitoring and/or recording of data while transmitted.
- Active Threats: Unauthor
- Threats
- Eavesdropping
- Password ``sniffing’’
- Data modification
- Spoofing (masquerading)
- Repudiation
- DDOS Attack
- Security Measures
- Password
- Encryption
- Digital Signature
- Firewall
- Blockchain
2. Cryptography
1). Cyptogorapy
- The field of study related to encoded information (comes from Greek word for “secret writing”)
- Encryption
- The process of converting plaintext into ciphertext
- Decryption
- The process of converting ciphertext into plaintext
2). Ciphers
-
Caesar Ciphers
-
Transposition Ciphers
3). Cyrptography
- Cipher
- Key
4). Cryptanalysis
5). Encryption & Decryption
- Encryption on computers
- Asymmetric Key Cryptography
- Symetric/Private Key Encryption
6). RSA Cryptography
- 참고자료(수업) : RSA Cryptography
- ENcr
7). Public/Private keys
- Applications of Pulbic and Private key
8). Standards
3. Other Applications of Public/Private Keys
- Digital Certificates
- Digital Signature
- How PGP Works - Encryption
[4]. Communication Performance Improvement
1.Performance Measurements
- Transmission Time = (Message Size)/(Channel Capacity)
- Response Time = MIT + MPT + MOT
- Waste Time = wait for available links at notes (Queuing Models)
- E.g., ATM card transactions (Asynchronous with parity bit) 1) Typing your PIN number (think time): 10 characters 2) Sending that information to the machine at the bank: 100 characters 3) Verifying your account and PIN number (application processing): .5 second함 4) Sending the result to the ATM terminal: 300 characters where typing speed = 5 characters/second and modem speed is 100 bps.
2. How to improve Efficiency
- Reduce Message Size: Compression
- Reduce Waiting Time: Multiplexing (Line Sharing)
- Avoid Bottleneck: Segmentation, Intelligent Routing(Packet Switching), Proxies(Local cache repositories)
- Prepare for Errors: Optimal Segmentation
compression과multiplexing이 가장 중요하기때문에 이 두개에 대해서만 언급, 또한
3. Compression
-
참고자료(수업) : Data Compression
- Reduces the size of data files to move more information with fewer bits
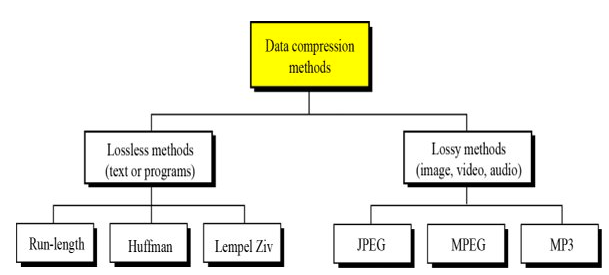
- Lossless comporession :
- Based on
code words:Huffman codes - Based on
dictionaries:Lemple-Ziv, Lemple-Ziv-Welch - Lossy :reconstituted data is only
perceptually equialent(jpeg, mpeg)
- Based on
- Huffman Decoding
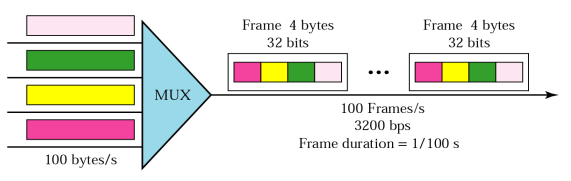
4. Multiplexing
1). Multiplexing(멀티플렉싱)이란?
- 참고자료(수업) : Multiplexing(6:07)
- Multiplexing : Simultaneous transmission techonology of multiple signals across a single data link.
- Multiplexer (MUX) : device that combines several signals into a single signal.
- Demultiplexer (DEMUX) : device that performs the inve rse operation.
- 참고이미지(수업) : ‘Direct to Direct’ 와 ‘Multiplexing’ 의 비교
Direct to Direct는에 비해 Multiplexing 기술
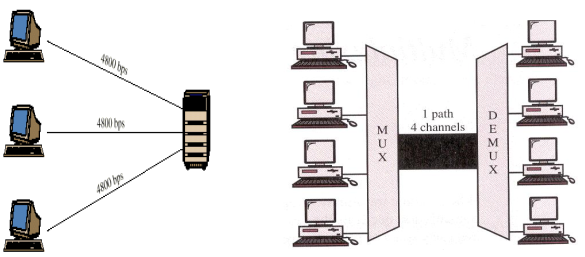
- Transmission Efficiency(전송효율)
- Several data sources share a common transmission medium, with each source having its own channel.
- Line sharing saves transmission costs.
- Higher data rates mean more cost-effective transmissions
- Most individual data sources require relatively low data rates
2). Multiplexing Technologies(1G-3G)
- Multiple Access Methods(1G, 2G, 3G)
- 참고이미지(수업) : FDMA, TDMA, CDMA의 비교
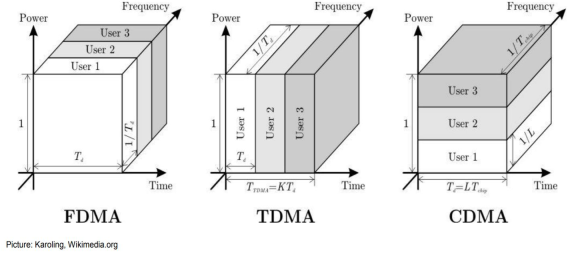
Frequency는 라디오처럼 터미널마다 각각 다른 주파수 할당, Time, Code
3). FDM : Frequency Division Multiplexing
- FDM이란?
Frequency는 라디오처럼 터미널마다 각각 다른 주파수 할당하는 방식.
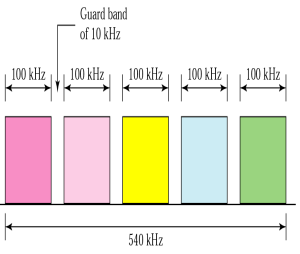
모든 주파수를 더한 것을 커버할만큼의 medium 이 필요함 - Guard band to separate channels (no interferences)
주파수를 합해서 보낼때 겹치는 대역이 생기는데 이를 방지하기 위해 사용하지 않는 대역으로 주파수를 구분해 주는 방법, 제일 낮은 주파수대역에서부터 제일 높은 주파수 대역을 스펙트럼이라 하며 데이터가 전송하는 부분을 Bandwidth 라고함. 이때 Guard band가 더해졌기 때문에 전체 주파수 대역인 Spectrum은 실제 Bandwidth보다 클 수밖에 없음.
고속도로의 차선과 같은 방법으로 Spectrum제한 때문에 채널 확장이 용이하지는 않지만 손쉬운 방법이고, 할당된 Bandwidth를 통해 중단없는 데이터를 보낼 수 있음
- 참고이미지(수업) : Guard band로 인한 Spectrum과 Bandwidth의 관계(Spectrum > Bandwidth)
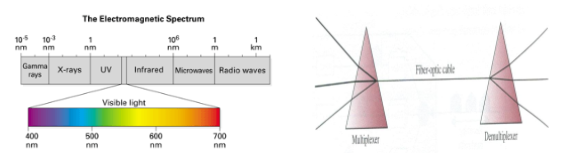
4). WDM : Wave-division Multiplexing
- WDM이란?
Fiber Optics 즉 광케이블에서는 전자기파장의 일부만 가시광선, 가시광선을 이용한 광케이블, 프리즘을 써서 MUX DEMUX로 활용할 수 있다.
-
참고이미지(수업) :
5). TDM : Time-Division Multiplexing
- TDM 이란??
예를들면 시간차를 두고 4개의 디바이스가 순서대로 데이터를 전송하는 방법(시간을 쪼개서 로테이션)
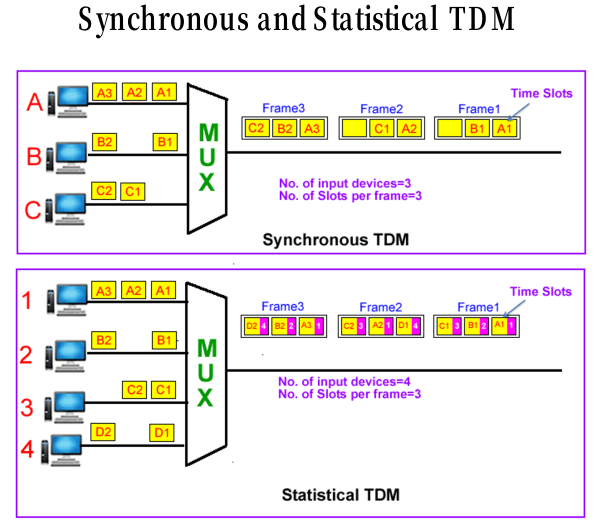
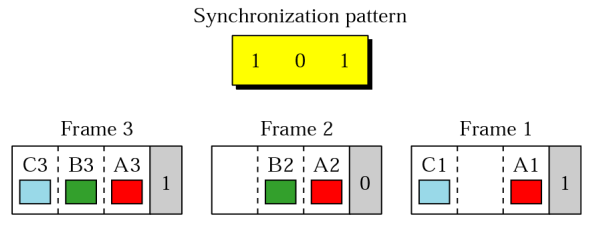
- Synchronous and Statistical TDM
Synchronous는 무조건 순서대로 데이터가 들어오는대로 보내기 때문에 비어있는 frame이 많아서 데이터 bandwidth에 LOSS가 많다.하지만 어느 터미널에서 데이터가 오는지 분명하게 확인할 수 있어 마킹이 필요 하지 않음. 반면에 statistical TDM은 빈 프레임이 없이 꽉꽉 채워서 보냄 하지만 어떤 터미널에서 오는것인지 슬롯에 마킹을 해줘야 함.
-
참고이미지(수업).1 :
-
참고이미지(수업).2 :
-
참고이미지(수업).3 :
- Synchronous TDM and PSTN
끊기지 않아야 하는 경우, 예를들면 서울-부산 사람들의 전화연결을 위해서는 Backbone 에 큰 Line을 두고 Multiplexing 한다. 신뢰할만한 통신네트워크를 묶어서 보증 하는 것-> T1, T3…
- Used in the modern digital telephone system
- US, Canada, Japan: DS-0, DS-1 (T-1), DS-3 (T-3), …
- Europe, elsewhere: E-1, E3, …
- Data rate of 1.544Mbps
- Uses PCM to digitize voice transmission at 8K/sec, frame length of 193bits
- Used in the modern digital telephone system
- SONET: Synchronous Optical Network
- Specification for high-speed digital transfer via optical fiber
- Rates from 51.84Mbps to 13.2Gbps
- Uses Synchronous TDM
6). CDMA
- CDMA?
QULCOMM 에서 개발, 우리나라에서 제일 먼저 상용화
- 정의 : 코드 분할 다중 접속(Code Division Multiple Access)
- 참고자료(수업) : CDMA
- 배경
내용 기존의 통신 방식인 주파수 분할 다중 접속(FDMA) 및 시간 분할 다중 접속(TDMA)는 다중 접속을 감당하는데 무리가 있다는 단점을 해결. 이론적으로는 동일한 무선 인터페이스를 이용하고 주파수 분배 방식만 다를 경우, FDMA, TDMA, CDMA 모두 동일한 전송 대역폭을 갖는다. 그러나 FDMA 방식이나 TDMA 방식의 경우 무선 통신중 발생할 수 있는 혼선을 방지하기 위해 물리적인 혼선 방지 영역[1]을 배치해야 하는데, 무선 통신 하면 카폰으로 이해하던, 과거 접속자 수가 얼마 없던 시절에는 분할할 일이 적기에 큰 불편 없이 썼지만 무선 통신 수요가 점증하는 상황에서 기존의 FDMA와 TDMA 방식으로는 무선 통신 수요가 몰리는 지역에선 통신에 사용되는 주파수보다 To improve the efficiency of transferring information over a shared communication line, messages are divided into fixed- sized, numbered packets요구량이 폭증하게 되리라는 것이 예견되었다.
-
장점
암호화 키를 잘 지키면 다른 사용자는 원래의 내용을 알수없어 보안성이 강하다고 알려졌으며[2], 물리적으로 더 이상 분할할 수 없는 지점까지만 수용 가능한 FDMA/TDMA와 다르게 접속자 수가 몰리면 그냥 음질을 낮춰 전송되는 정보량을 줄여버리면 그만인 CDMA는 높은 통화 효율과 안정적인 통화 서비스 제공을 보장할 수 있다.
당시의 기술 수준으로도 여러 주파수 조각 중 원하는 조각을 선별해 수신해야 하는 기존 방식보다 일단 송출되는 주파수를 다 받기에 Diversity 측면에서 우수성을 인정받았으며, 이로 인해 페이딩 에 강하다. CDMA 도입 당시에 언론에서 자주 하던 말인 산악이 70%인 한국 지형에 강하다는 이를 두고 한 말이다. Soft Handoff를 구현하려 여러 기술적 묘기가 필요했던 기존 기술과는 달리 그냥 이동국이 접속한 기지국의 인접 기지국에서도 통신정보를 동시에 송출하면 Soft Handoff 구현 가능. 이 때 이용된 기지국 간의 유연한 접속 기술은 CDMA의 장점이 발휘되기 어려운 업링크 환경에서 혼잡하지 않은 기지국과 통신하는 기술로도 유용하게 사용되었다.
-
참고이미지(수업) :
-
- 원리
CDMA는 주파수, 시간이라는 물리적인 혼선 방지를 코드라는 논리적인 혼선 방지책으로 전환하는 방법으로 이 문제를 해결하였다. CDMA를 이해하려면 DSSS를 먼저 반드시 알아야 하지만 대략적인 아이디어만 간단히 서술하자면, 기지국 내의 사용자들에게 전송해야 할 데이터를 사용자가 알고 있는 암호(Code)로 각각 암호화 한 후, 모두 더해서 방송 송출하듯이 전송. 사용자는 자신이 갖고 있는 암호키로 데이터를 복호화 하고 다른 사용자의 신호 성분은 잡음으로 수신되거나, 코드 벡터의 직교성과 내적의 원리를 사용해 다른 사용자의 신호를 자연스럽게 무시하는 원리이다.
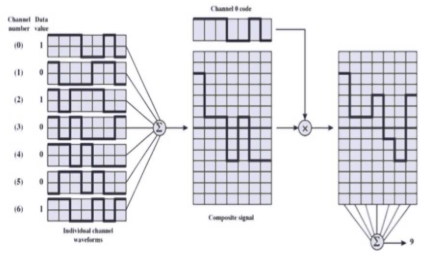
- CDMA Spread code 가 중요
- 1/0을 각 채널마다 7bit의 Spread code로 변환하여 신호를 보냄
- Channel Code
- 1 Channel Spreading Code
- 0 Inversion Spreading
- Composite Signal
frequency division을 동시에 보낸다는것은 analog signal에서 interference가 일어나는데 통신에는 cell이라고 해서 반경마다 서울에서 보내는것, 부산에서 보내는것은 interference가 없다. 따라서 CDMA는 frequency division도 하는 것은 인접해서 하는 것은 같은 frequency를 같이 써도 된다. 즉 간섭을 없애기 위해 cell을 쪼개서 frequency division + code division 의 방식이다.
- CDMA Spread code 가 중요
5. Segmentation
- Why Do Segmentation?
- Error Possibility
- Reduce Waiting Time on the network
- Tradeoff
6. 5G 참고
정리하자면, 통신에서 Peformance를 높이기 위한 3가지 방법으로는,
1.보내는 양을 줄여서 보내는 compression
- 라인을 잘 활용하기 위해 묶어서 보내는 multiplexing
- 라인의 스피드나 에러확률에 따라서 그때그때마다 waiting(queing)타임을 줄이기 위한 segmentation
Leave a comment