BMC : Basics of Telecommunications(3)
BASICS OF Business Data Communication(3) :Networks
Switching Technologies 가 중요하다.
[1]. Networks
1. Digital Commnication Networks
- 네트워크의 범위
- Distance에 따라 LAN/WAN
- 컴퓨터 네트워크
- Wireless
- Terminology
- Network Components
2. Internet
- Structure of the Internet
- Connecting to Internet Backbone
- 동시 접속자에 dynamic 하게 ip address를 할당
- LIne Contentions
3. Networking
1). Server/Client model
- Computer networks have opened up an entire frontier in the world of computing called the client/server model
2). Networking
- File server : A computer that stores and manages files for multiple users on a network
- Web server : A computer dedicated to responding to requests (from the browser client) for web pages
- Node(Host) / Data transfer rate /
3). Networking Devices
- Hub
- Switches
- Router
2. Data Flows
- Simplex : One way only
[2]. LAN
1. Types of Networks
1). 네트워크
- Local-area network (LAN) A network that connects a relatively small number of machines in a relatively close geographical area
- Types (Topology) of LAN
- 참고자료(수업) : LAN
2). 종류 (Various Configuration called toplogies)
-
Ring topology : A configuration that connects all nodes in a closed loop on which messages travel in one direction
-
Star topology : A configuration that centers around one node to which all others are connected and through which all messages are sent
-
Bus topology(Ethernet) : All nodes are connected to a single communication line that carries messages in both dire*ctions
2. MAC (Medium Access Control)
- 참고자료(수업) : Medium Access Control
| Toplogy/MAC | BUS | Tree/Star | Ring |
|---|---|---|---|
| CSMA/CD | O | O | |
| Token Bus | O | O | |
| Token Ring | O |
3. CSMA/CD
CSMA/CD 특징 : 반송파를 감지하는 기법을 사용한다. 데이터를 보내고자 하는 송신자 ‘A’ 는 수신자 ‘B’ 가 이미 다른 송신자 ‘C’ 와 통신을 중임을 감지하면 즉시 통신을 중단하고 정체신호 (Jam Signal)을 보낸다. 그리고 임의의 시간 동안 대기하면서 재전송할 준비를 한다. 일단, 정체 신호가 발생하면 송신자 ‘A’ 뿐만 아니라, 수신자 ‘B’ 로 데이터를 보내고자 하는 네트워크 상의 모든 노드 들에게 전달된다. 이로써 불필요한 전송을 사전에 차단시켜 트래픽을 줄인다. CSMA/CD 방식은 OSI 계층에서 2계층에 속하지만, OSI 7계층 모델의 프로토콜은 아니다.
주요 절차 : 전송을 위한 프레임을 준비한다. 매체가 사용이 가능한가? 만일 아니라면, 사용이 가능할 때까지 대기한다. 전송을 시작한다. 충돌이 일어났는지 확인하고 만일 그렇다면, 충돌 탐지 절차로 이동한다. 재전송 계수기를 초기화 하고 프레임 전송을 종료한다.
충돌 탐지 시 절차 : 정체 신호가 전체 송신자에게 전달되도록 하기 위해 최소 패킷전송시간 까지 전송을 계속한다. 재전송 계수기의 재전송 시도횟수를 증가시킨다. 임의의 시간동안 대기한다. 첫 번째 단계부터 반복한다. 충돌 탐지 방법은 매체에 의존한다. 그러나 이전 버전의 이더넷과 같은 전자적인 버스에서, 충돌은 송신자가 보낸 데이터와 수신자가 받은 데이터를 비교해봄으로써 탐지가 가능하다. 만일 두 가지가 다르다면 다른 송신자 측에서 보낸 데이터를 덮어씌웠다는 것을 의미한다. 프레임 전송 중에 충돌을 감지했다면, 전송은 즉시 중단된다. 대신 정체신호를 네트워크 상에 있는 전체 노드들에게 전송하면서 충돌 여부를 확정하게 된다.
4. Token Bus
5. CSMA/CD vs Token Bus
-
참고이미지 및 링크 : 매체접근방식
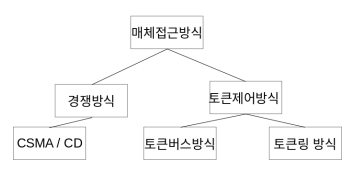
-
분류
매체접근방식 BUS Tree/Star Ring CSMA/CD O O Token Bus O O Token Ring O -
특징
- Under heavy loads, CSMA/CD performs poorly.
- Deterministic delay in token bus: important for process control
- Priority can be assigned in token bus
- Complexity of Token bus
- Token bus uses broadband (analog) transmission
6. Token Ring (IEEE 802.5)
빈 토큰(빈 패킷)이 미리 돌고 있으면 스테이션에서 아무 것도 없으면 데이터를 로딩해서 보낸다. 전송완료가 되면 마킹을 바꿔서 다른 패킷이 사용 할 수 있다. 순서는 없고 도는 속도가 빨라야지, 빈 패킷기다리는데 오래 걸리면 안되기 때문에 optical 네트워크에서만 이런 방식을 사용함.
- Token packet circulates when all stations are idle
- If you want to transmit, wait for a free token
- Grab free token, transform it into a control field, append to data and send out
- After round trip, insert a free token
- Only one data packet at a time.
7. FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface)
질문사항 : ETHERNET FDDI?
[3]. WAN : Wide-Area Network
와이드 랜에는 몇백만개 오백억개가 넘기 때문에 리스트 만들어서 순서 기다리라고 하는건 불가. 즉 LAN에서 쓰는 방식은 WAN 에서 못씀.
1. Wide-area network (WAN) :
1). WAN이란?
- A network that connects two or more local-area networks over a potentially large geographic distance
- Often one particular node on a LAN is set up to serve as a gateway to handle all communication going between that LAN and other networks
- Communication between networks is called internetworking
- The Internet, as we know it today, is essentially the ultimate wide-area network, spanning the entire globe.
- Simplex : One way only
2). Who owns the Internet?
- No single person or company owns the Internet or even controls it entirely. As a wide-area network, it is made up of many smaller networks. These smaller networks are often owned and managed by a person or organization. The Internet, then, is really defined by how connections can be made between these networks.
2. Type of networks
3. Packet Switching
하나의 메시지를 보내는건 너무 양이 많기 때문에 메시지를 패킷단위로 나눠서 보낸다. WAN에서는 스위칭 기술이 네트워크를 연결해 주는 기술이다.
- To improve the efficiency of transferring information over a shared communication line, messages are divided into fixed-sized, numbered packets
- Network devices called routers are used to direct packets between networks
-
참고이미지(수업) :
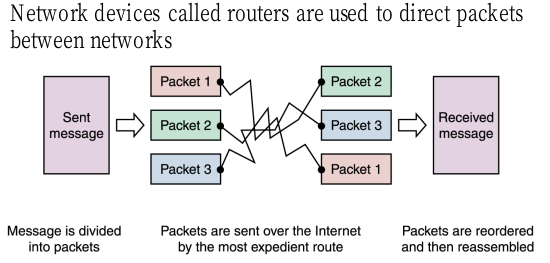
4. Open Systems
-
Proprietary system : A system that uses technologies kept private by a particular commercial vendor(One system couldn’t communicate with another, leading to the need for)
-
Interoperability : The ability of software and hardware on multiple machines and from multiple commercial vendors to communicate
-
Open systems : Systems based on a common model of network architecture and a suite of protocols used in its implementation
4. OSI
OSI는 제품이 아니고 표준 가이드라인임 by ISO
- OSI
|LAYER|DESCRIPTION| |:—:|—| |7|Application layer| |6|Presentation layer| |5|Session layer| |4|Transport layer| |3|Network layer| |2|Data link layer| |1|Physical layer|
5. Network Protocls
- Network protocols are layered such that each one relies on the protocols that underlie it. Sometimes referred to as a protocol stack
-
참고이미지(수업) : Network Protocols
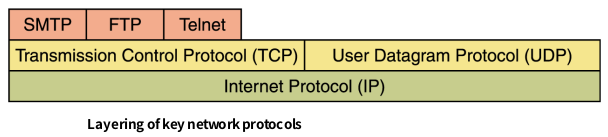
- The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) established the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Reference Model
- Each layer deals with a particular aspect of network communication
5. TCP/IP
- TCP/IP
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) : TCP software breaks messages into packets, hands them off to the IP software for delivery, and then orders and reassembles the packets at their destination
- IP (Internet Protocol) : IP software deals with the routing of packets through the maze of interconnected networks to their final destination
-
TCP/IP Structure
Layer Things to do Process (Application) Telnet, FTP, SMTP Host-to-Host (TCP,Session) Reliability and Efficiency, Security Internet (Transport) Routing NAP Host-Network -
Networking Protocol :TCP/IP Examples
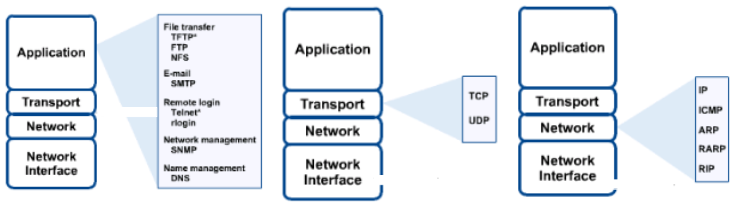
IP는 길찾기 하는 역할
6. UDP : User Datagram Protocol
- It is an alternative to TCP
- The main difference is that TCP is highly reliable, at the cost of decreased performance, while UDP is less reliable, but generally faster
7. High-Level Protocols
- Other protocols build on the foundation established by the
TCP/IP protocol suite
- SMTP : Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- FTP : File Transfer Protocol
- Telnet :
- http : Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
8.MIME : Multipurpose Internet Mail Extension
메일은 텍스트로만 되어 있었는데 signature 등이 추가되어서 extension 됨. 네트워크요청시 어떤 request 인지를 specify 해주는게 port 임, Protocol은 단순 그냥 앱이라고 보면 됨
1). MIME
- Related to the idea of network protocols and standardization is the concept of a file’s MIME type
- Based on a document’s MIME type, an application program can decide how to deal with the data it is given
- Protocol/Port
2). MIME Type
- Type |Protocol|Port| |—|—| |Echo|7| |File Transfer Protocol(FTP)|21| |Telnet|23| |Simple Mail Transfer Protocol(SMTP)|25| |Domain Name Service(DNS)|53| |Gopher|70| |Finger|79| |Hyper Text Transfer Protocol(HTTP)|80| |Post Office Protocol(POP3)|110| |Network News Transfer Protocol(NNTP)|119| |Internet Relay Chat(IRC)|6667|
9 Firewalls
들어오는 Request를 보고 판단한다. 네트워크상의 서버인데 보안솔루션 잔뜩 깔려져 있는 서버
-
Firewalls : A machine and its software that serve as a special gateway to a network, protecting it from inappropriate access
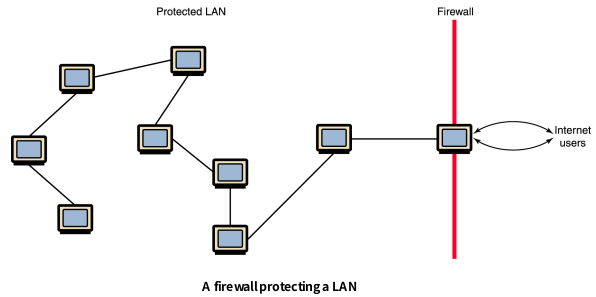
- Filters the network traffic that comes in, checking the validity of the messages as much as possible and perhaps denying some messages altogether
- Enforces an organization’s access control policy
10. Routing
tcp/ip이 ip가 라우팅을 하는 것임
- 참고자료(수업) : Connecting between diffrent protocols
[4]. Switching Technologies
패킷스위칭은 두가지 방식으로 WLN 데이터그램, 버츄얼서킷방식이 있다. 우리가 매일 쓰는게 버츄얼
1. Switching Technology: Saving Links but Securing a Path
-
그림
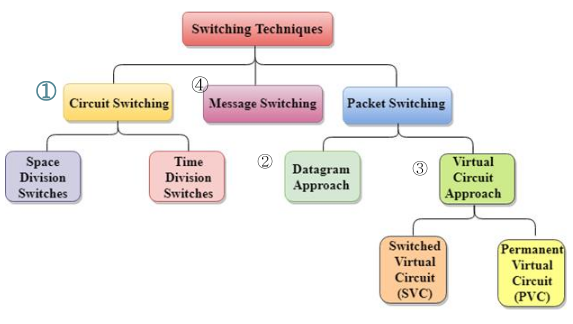
-
Two different switching technologies
- Circuit switching
- Packet switching
2. Circuit Switching
- Public Circuit Switched Network : One way only
- [그림]
동시 접속자만큼 쓸때마다 롱디스턴스 라인을 연결해줌(자동접속기가)
- [그림]
3. Packet switching
1). Packet Switching Principles
2). Packet Switching Technique
4. Datagram
동영상 zoom 같은거는 순서가 제대로 들어오는것이 중요하다. 리셔플링불가
5. Virtual Circuit
순서가 뒤바뀌지 않게 가는길을 하나로 fix, 1,2,3번은 가는 line만 가기 때문에 순서가 바뀔일은 없다. VPN
6. Datagram vs Virtual Circuit
- Virtual circuits
- Network can provide sequencing (packets arrive at the same order) and error control (retransmission between two nodes).
- Packets are forwarded more quickly
- Based on the virtual circuit identifier
- No routing decisions to make
- Less reliable
- If a node fails, all virtual circuits that pass through that node fail.
- Datagram
- No call setup phase
- Good for bursty data, such as Web applications
- More flexible
- If a node fails, packets may find an alternate route
- Routing can be used to avoid congested parts of the network
- No call setup phase
-
Comparison of communication switching techniques
Circuit Switching Datagram Packet Switching Virtual Circuit Switching Dedicated transmission path No dedicated path No dedicated path Continuous transmission of data Transmission of packets Transmission of packets Fast enough for interactive Fast enough for interactive Fast enough for interactive Messages are not stored Packets may be stored until delivered Packets stored until delivered THe path is estabilished for entire conversation Route estabilished for each packet Route estabilished for entire conversation Call setup delay; negligible transmission delay Packet transmission delay Call setup dealy; packet transmission delay Busy signal if called party busy Sender may be notified if packet not delivered Sender notified of connection denial Overload may block call setup; no dealy for estabilised calls Overload increses packet dealy OVerlaod may block call setup; increses packet dealy Electromechanical or computerized switching nodes Small switching nodes Small switching nodes User responsible ofr message loss protection Network may be responsible for individual packets Network may be responsible for packet sequences Usually no speed or code conversion Speed and code conversion Speed and code conversion Fixed bandwidth Dynamic use of bandwidth Dynamic use of bandwidth No overhead bits after call setup Overhead bits in each packet Overhead bits in each packet
[5]. Internet
1. Internet Connections
-
Internet backbone A set of high-speed networks that carry Internet traffic These networks are provided by companies such as AT&T, GTE, and IBM
-
Internet service provider (ISP) A company that provides other companies or individuals with access to the Internet
- Various technologies available that you can use to connect a home computer to the Internet
- A phone modem converts computer data into an analog audio signal for transfer over a telephone line, and then a modem at the destination converts it back again into data
- A digital subscriber line (DSL) uses regular copper phone lines to transfer digital data to and from the phone company’s central office
- A cable modem uses the same line that your cable TV signals come in on to transfer the data back and forth
-
Broadband
- Internet 접속 예시
- Transaction control protocol/ internet protocol
- IP address and domain name server (DNS)
- 137.68.237.20 deerlab.Kaist.Ac.Kr
- Datagram switching technology
-
IP Address
- Domain Names
2. URL :
웹이 나오면서 PORT를 따로 관리 하는게 아니라 Uniform 하게 인터넷상에 붙어있는 모든 컨텐츠를 하나의 방식으로 찾아가는 주소 표준이다. 앞에는 프로토콜이름, 도메인서버이름, 옵셔널포트이름, filepath
URL(Uniform Resource Locator 또는 web address, 문화어: 파일식별자, 유일자원지시기)은 네트워크 상에서 자원이 어디 있는지를 알려주기 위한 규약이다. 즉, 컴퓨터 네트워크와 검색 메커니즘에서의 위치를 지정하는, 웹 리소스에 대한 참조이다. 흔히 웹 사이트 주소로 알고 있지만, URL은 웹 사이트 주소뿐만 아니라 컴퓨터 네트워크상의 자원을 모두 나타낼 수 있다. 그 주소에 접속하려면 해당 URL에 맞는 프로토콜을 알아야 하고, 그와 동일한 프로토콜로 접속해야 한다.
FTP 프로토콜인 경우에는 FTP 클라이언트를 이용해야 하고, HTTP인 경우에는 웹 브라우저를 이용해야 한다. 텔넷의 경우에는 텔넷 프로그램을 이용해서 접속해야 한다.
URL은 제일 앞에 자원에 접근할 방법을 정의해 둔 프로토콜 이름을 적는다. gopher, telnet, ftp, http, usenet 등이다. 프로토콜 이름 다음에는 프로토콜 이름을 구분하는 구분자인 “:”을 적는다. 만약 IP 혹은 Domain name 정보가 필요한 프로토콜이라면 “:” 다음에 “//”를 적는다. 프로토콜명 구분자인 “:” 혹은 “//” 다음에는 프로토콜 마다 특화된 정보를 넣는다.
- 예1) http://www.somehost.com/a.gif - IP 혹은 Domain name 정보가 필요한 형태 ( www.somehost.com에 있는 a.gif를 가리키고 있음 )
- 예2) ftp://id:pass@192.168.1.234/a.gif - IP 혹은 Domain name 정보가 필요한 형태 ( 192.168.1.234에 있는 a.gif를 가리키고 있음 )
- 예3) mailto:somebody@mail.somehost.com - IP정보가 필요없는 프로토콜 ( mailto 프로토콜은 단지 메일을 받는 사람의 주소를 나타냄 )
- URL identifies a specific resource on a server in a domain
- URL tells what protocol to use to access the resource
- URL format: http://deerlab.kaist.ac.kr:1024/program/courses/index.shtml protocol://domain_name[:port] /path_name/file_name
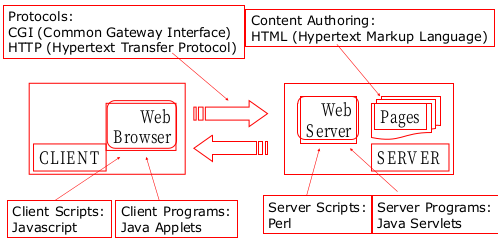
3. WEB
월드 와이드 웹(World Wide Web, WWW, W3)은 인터넷에 연결된 컴퓨터를 통해 사람들이 정보를 공유할 수 있는 전 세계적인 정보 공간을 말한다. 간단히 웹(Web)이라 부르는 경우가 많다. 이 용어는 인터넷과 동의어로 쓰이는 경우가 많으나 엄격히 말해 서로 다른 개념이다. 웹은 전자 메일과 같이 인터넷 상에서 동작하는 하나의 서비스일 뿐이다. 그러나 1993년 이래로 웹은 인터넷 구조의 절대적 위치를 차지하고 있다. 인터넷에서 HTTP 프로토콜, 하이퍼텍스트, HTML형식 등을 사용하여 그림과 문자를 교환하는 전송방식을 말하기도 한다.
인터넷상의 정보를 하이퍼텍스트 방식과 멀티미디어 환경에서 검색할 수 있게 해주는 정보검색 시스템이다. 하이퍼텍스트 형식으로 표현된 인터넷상의 다양한 정보를 효과적으로 검색하는 시스템으로 전 세계적으로 가장 널리 보급되어 있다.
하이퍼텍스트는 웹 브라우저라 불리는 프로그램을 통해 웹 서버에서 “문서”나 웹 페이지등의 정보 조각을 읽어들여 컴퓨터 모니터에 출력하는 형태로 보이게 된다. 그러고 나서 사용자는 각 페이지에 있는 하이퍼링크를 따라 다른 문서로 이동하거나, 그 페이지를 서비스하고 있는 서버로 일련의 정보를 보낼 수도 있다. 하이퍼링크를 따라 이동하는 행위를 흔히 웹 서핑(web surfing, 문화어: 망유람[2]) 또는 웹 브라우징이라 한다. 그리고 관련된 내용들이 모여있는 웹 페이지들의 집합을 웹 사이트라 한다. 영어 단어 월드와이드(worldwide)는 보통 공백이나 하이픈 없이 한 단어로 쓰이지만, 월드 와이드 웹(World Wide Web)과 그 약어인 WWW는 공식적인 영어 낱말로 사용되고 있다.
월드 와이드 웹은 다음의 세가지 기능으로 요약할 수 있겠다. 첫 번째 통일된 웹 자원의 위치 지정 방법 예를 들면 URL. 두 번째 웹의 자원 이름에 접근하는 프로토콜(protocol) 예를 들면 HTTP, 세 번째 자원들 사이를 쉽게 항해 할 수 있는 언어 예를 들면 HTML
- WEB Architecture
4. Client/server
5. HTTP
HTTP(HyperText Transfer Protocol)는 WWW 상에서 정보를 주고받을 수 있는 프로토콜이다. 주로 HTML 문서를 주고받는 데에 쓰인다. TCP와 UDP를 사용하며, 80번 포트를 사용한다.
HTTP는 클라이언트와 서버 사이에 이루어지는 요청/응답(request/response) 프로토콜이다. 예를 들면, 클라이언트인 웹 브라우저가 HTTP를 통하여 서버로부터 웹페이지나 그림 정보를 요청하면, 서버는 이 요청에 응답하여 필요한 정보를 해당 사용자에게 전달하게 된다. 이 정보가 모니터와 같은 출력 장치를 통해 사용자에게 나타나는 것이다.
HTTP를 통해 전달되는 자료는 http:로 시작하는 URL(인터넷 주소)로 조회할 수 있다.
- Evolution of Computing
- HTTP Protocol
- Web Clients and Servers
- HTTP Communication
- Putting it All Together
- HTTP Is Stateless
- Location of Web Contents
- 예시
- Browser
- Game of Eyeballs
- Cyber-Identity
[6]. IoT and LoRa
1. Introduction
- KEY FEATURES OF THE TECHNOLOGY
- COVERAGE IN 2017
- SMART IoT SOLUTIONS – B2B
- Environment :
- Utility :
- Municipal :
- Infrastructure :
- Industry :
- Technological comparison of IoT networks in CR
2. Different Wireless Technologies
- LoRaWAN Performance(cont.)
- LoRa Architecture
- Three classes of End Devices
- Activation
3. LoRa Technology
- Introduction(cont.)
- How it works?
- LoRa modulation
-
LoRaWAN network protocol
- Low Power Wide Area Network(LPWAN)
Leave a comment